Transform-both-sides Box-Cox transformation
boxcox.drc.RdFinds the optimal Box-Cox transformation for non-linear regression.
# S3 method for drc boxcox(object, lambda = seq(-2, 2, by = 0.25), plotit = TRUE, bcAdd = 0, method = c("ml", "anova"), level = 0.95, eps = 1/50, xlab = expression(lambda), ylab = "log-Likelihood", ...)
Arguments
| object | object of class |
|---|---|
| lambda | numeric vector of lambda values; the default is (-2, 2) in steps of 0.25. |
| plotit | logical which controls whether the result should be plotted. |
| bcAdd | numeric value specifying the constant to be added on both sides prior to Box-Cox transformation. The default is 0. |
| method | character string specifying the estimation method for lambda: maximum likelihood or ANOVA-based (optimal lambda inherited from more general ANOVA model fit. |
| eps | numeric value: the tolerance for lambda = 0; defaults to 0.02. |
| level | numeric value: the confidence level required. |
| xlab | character string: the label on the x axis, defaults to "lambda". |
| ylab | character string: the label on the y axis, defaults to "log-likelihood". |
| … | additional graphical parameters. |
Details
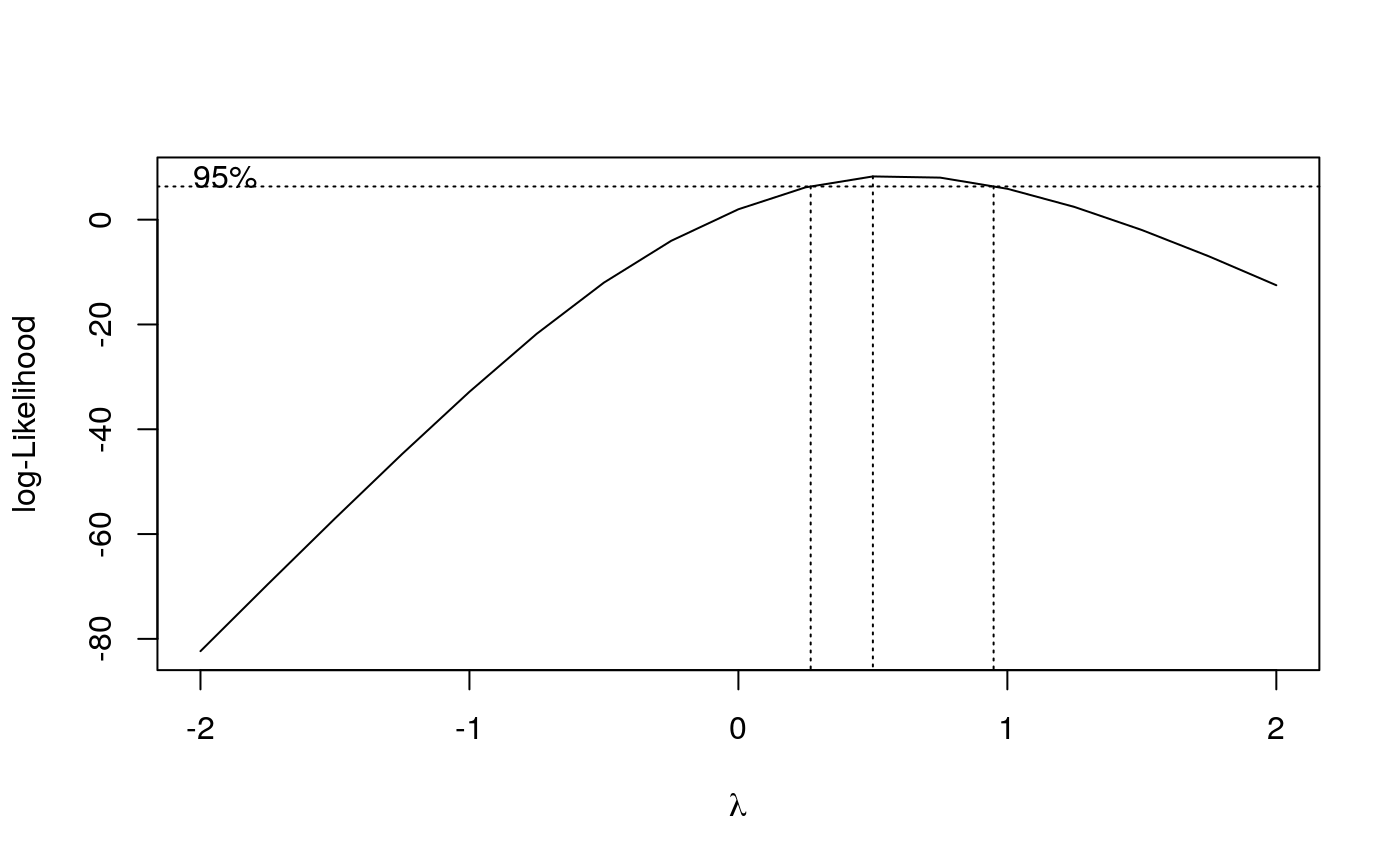
The optimal lambda value is determined using a profile likelihood approach: For each lambda value the dose-response regression model is fitted and the lambda value (and corresponding model fit) resulting in the largest value of the log likelihood function is chosen.
Value
An object of class "drc" (returned invisibly). If plotit = TRUE a plot of loglik vs lambda is shown indicating a confidence interval (by default 95 the optimal lambda value.
References
Carroll, R. J. and Ruppert, D. (1988) Transformation and Weighting in Regression, New York: Chapman and Hall (Chapter 4).
See also
For linear regression the analogue is boxcox.
Examples
## Fitting log-logistic model without transformation ryegrass.m1 <- drm(ryegrass, fct = LL.4()) summary(ryegrass.m1)#> #> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (4 parms) #> #> Parameter estimates: #> #> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value #> b:(Intercept) 2.98222 0.46506 6.4125 2.960e-06 *** #> c:(Intercept) 0.48141 0.21219 2.2688 0.03451 * #> d:(Intercept) 7.79296 0.18857 41.3272 < 2.2e-16 *** #> e:(Intercept) 3.05795 0.18573 16.4644 4.268e-13 *** #> --- #> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 #> #> Residual standard error: #> #> 0.5196256 (20 degrees of freedom)## Fitting the same model with the optimal Box-Cox transformation ryegrass.m2 <- boxcox(ryegrass.m1)#> Warning: NaNs produced#> Warning: NaNs produced#> Warning: NaNs produced#> Warning: NaNs producedsummary(ryegrass.m2)#> #> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (4 parms) #> #> Parameter estimates: #> #> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value #> b:(Intercept) 2.61839 0.39151 6.6880 1.649e-06 *** #> c:(Intercept) 0.39083 0.10429 3.7474 0.001269 ** #> d:(Intercept) 7.86633 0.29558 26.6136 < 2.2e-16 *** #> e:(Intercept) 3.01662 0.21005 14.3612 5.354e-12 *** #> --- #> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 #> #> Residual standard error: #> #> 0.2962958 (20 degrees of freedom) #> #> Non-normality/heterogeneity adjustment through Box-Cox transformation #> #> Estimated lambda: 0.5 #> Confidence interval for lambda: [0.269,0.949] #>